Loudspeakers have been an integral part of our lives for many decades, allowing us to enjoy music, movies, and other forms of audio entertainment. While we may associate their quality with factors like speaker size, design, and amplification, one crucial component often goes unnoticed: magnetic materials. These materials play a significant role in the functioning and performance of loudspeakers, influencing sound quality, efficiency, and overall user experience. In this blog, we will delve into the world of magnetic materials and explore how they contribute to the remarkable audio experience provided by today's loudspeakers.
1.The Role of Magnetic Materials in Loudspeakers:
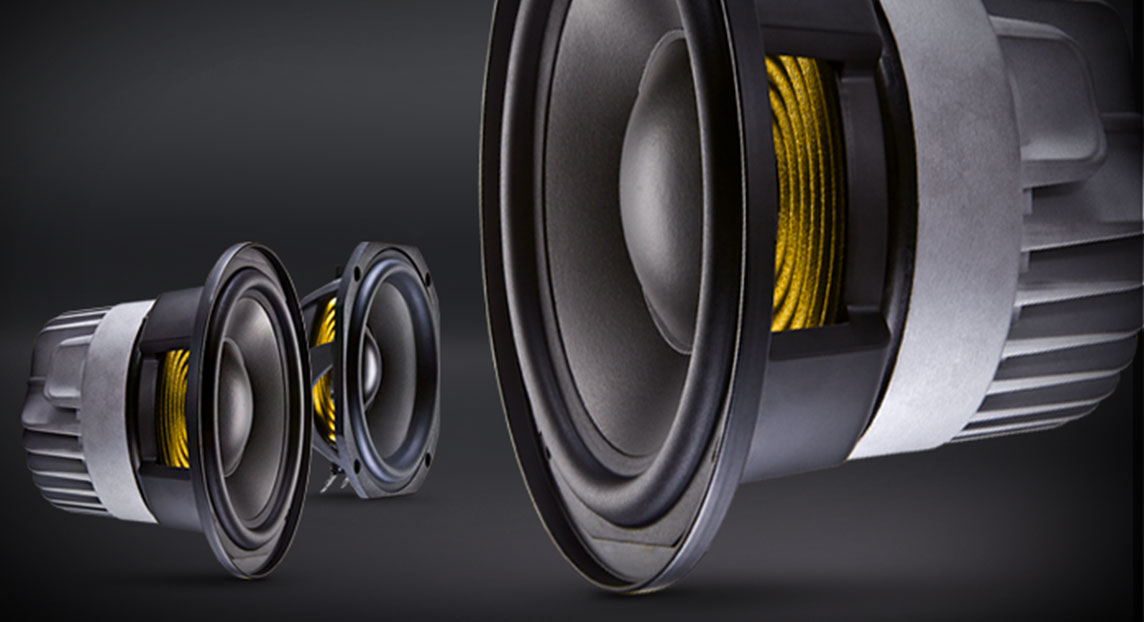
Magnetic materials are used extensively in loudspeakers to convert electrical signals into sound waves that we can hear. The basic principle revolves around electromagnetic induction, where an electrical current passing through a coil of wire creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnet in the loudspeaker, causing the coil to move back and forth rapidly, thus generating sound waves.
The choice of magnetic material greatly affects the efficiency and performance of loudspeakers. One commonly used material is neodymium, a rare-earth magnet with exceptional magnetic properties. Neodymium magnets offer high magnetic field strength while being compact, making them ideal for miniaturized loudspeakers found in portable devices like smartphones and earphones. Their strength allows for greater sensitivity, ensuring clear and accurate sound reproduction even from small speakers.
Another key magnetic material found in loudspeakers is ferrite, a type of ceramic magnetic material. Ferrite magnets possess excellent stability and are highly resistant to temperature changes, making them a reliable choice for larger loudspeakers used in home audio systems and professional applications. They are cost-effective and provide a balanced audio response without compromising on sound quality.
AlNiCo magnet was the first magnetic materials used for loudspeakers. Its disadvantage is that the power is small, the frequency range is also narrow, hard and very brittle, processing is very inconvenient, in addition to cobalt is a scarce resource, AlNiCo price is relatively high. From the cost-effective point of view, the choice of AlNiCo magnet is relatively small.
2.Enhancing Sound Quality:
The magnetic materials used in loudspeakers not only contribute to their functionality but also play a crucial role in achieving superior sound quality. Advanced materials like neodymium enable loudspeakers to produce clearer, more detailed, and dynamic sound due to their higher power handling capabilities and improved transient response. Such materials ensure that the audio signal is accurately reproduced, resulting in a more immersive and enjoyable listening experience.
3.Efficiency and Power Handling:
Efficiency is another critical aspect influenced by the choice of magnetic materials in loudspeakers. Neodymium magnets, for instance, offer high energy conversion efficiency, allowing devices to operate with lower power requirements. This efficiency translates to longer battery life for portable devices and reduced power consumption for home audio systems. Furthermore, powerful magnets like neodymium enable louder sound output while maintaining low distortion levels, making them indispensable for applications where high sound pressure levels are desired, such as professional sound systems.
4.Future Innovations:
As technology advances, researchers and engineers continuously strive to push the boundaries of loudspeaker design. New magnetic materials with improved magnetic strength, better linearity, and reduced size are being developed, paving the way for even more compact and efficient loudspeakers in the future. The evolution of materials, such as rare-earth alloys and composite magnets, holds the potential to revolutionize the audio industry and create more immersive sonic experiences for users.
Post time: Aug-30-2023
